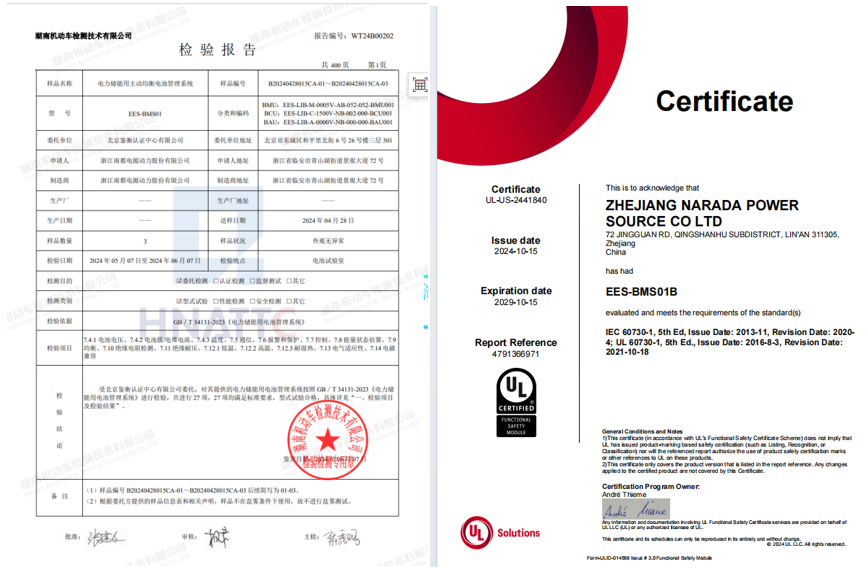
The BMS is an essential component for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of new energy storage systems. Recently, Narada Power’s newly developed 1500V liquid cooling active balancing BMS system for energy storage obtained the CGC type test report under GB34131-2023 and IEC/UL60730 functional safety certification reports and certificates, qualifying it for sale in domestic, European, and American markets.
In recent years, energy storage BMS technology has advanced toward distributed, multi-layered management frameworks and active balancing techniques, addressing complex technical challenges such as cell temperature monitoring and internal state calculations. Narada Power has continuously monitored these needs and, leveraging AI and big data, has developed a state-of-the-art 1500V liquid cooling active balancing BMS system.
This system features core advantages of standardization, modularity, and intelligence. Through a four-layer architecture—Data Acquisition Layer, Charge-Discharge Control Layer, System Management Layer, and Cloud Service Layer—it enables comprehensive, lifecycle management of energy storage batteries from all dimensions.

Data Acquisition Layer
The data management layer of Narada’s BMS gathers cell voltage and temperature data with active balancing functionality to ensure consistency across cells.
The system’s automotive-grade battery management chip design guarantees high precision and reliability across the system's lifecycle. Furthermore, the temperature collection circuitry includes a three-layer protection design, effectively minimizing the risk of chip failure in temperature sensing.
Additionally, Narada’s BMS incorporates a bi-directional DC-DC active balancing function, enabling energy transfer between individual cells based on SOC differences. This solution enhances balancing accuracy and efficiency, supporting optimized operation of energy storage batteries over their entire lifecycle.
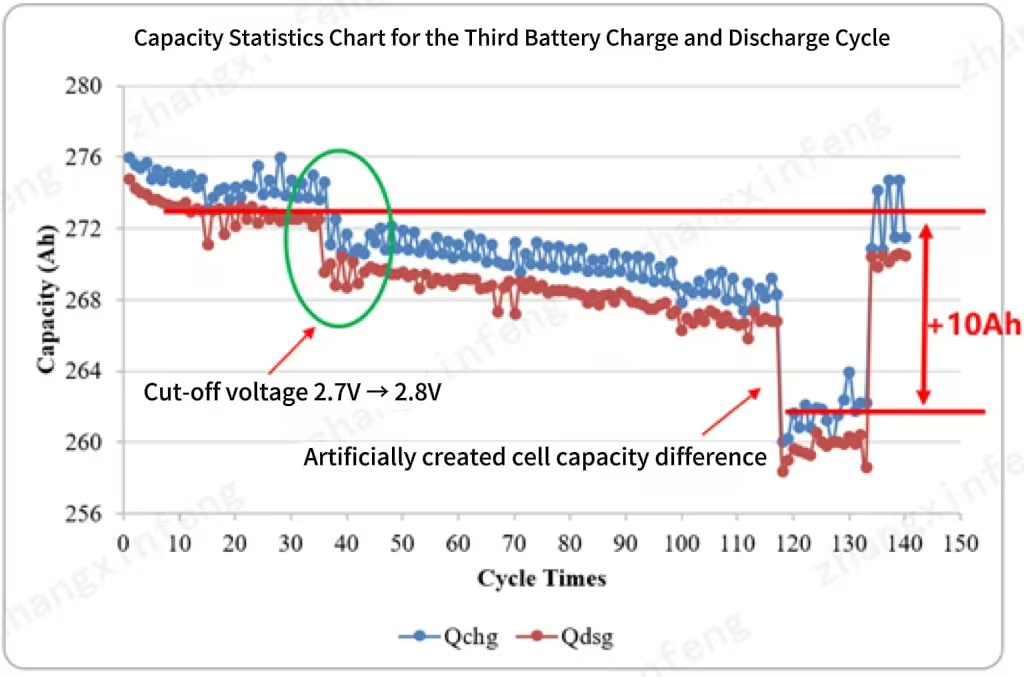
Zhou Gang, Director of Narada’s Electric Control Research Institute, explained, “To test the BMS’s active balancing capabilities, we created a 6Ah capacity differential within the system. After enabling active balancing, our tests showed a 10Ah increase in discharge capacity within 24 hours, which not only compensated for the 6Ah cell discrepancy but also largely mitigated long-term capacity imbalances. The balancing effect is remarkably significant.”
Charge-Discharge Control Layer
The Charge-Discharge Control Layer is responsible for managing the charging and discharging processes of battery clusters. It provides real-time estimation of the battery's state of charge (SOX) and ensures that the battery is neither overcharged nor overdischarged, implementing a three-tier protection system with primary, secondary, and tertiary alerts.
Based on the integration of core technologies, Narada’s energy storage BMS has demonstrated a voltage and current collection accuracy of 0.2% (industry standard is 1%), with zero drift current less than 10mA, reaching measurement-level precision. These collection accuracies are far superior to industry standards, providing a solid foundation for high-precision SOC estimation.
Zhou Gang explained that Narada’s SOC estimation is based on ampere-hour integration. It incorporates dynamic, static, special charge-discharge regions, and full charge/discharge corrections across multiple dimensions and operational conditions, fully meeting the power requirements for peak shaving and frequency regulation in energy storage stations based on the battery's SOC.
System Management Layer
The System Management Layer is responsible for gathering and storing local data, enabling human-machine interaction, parameter settings, and multi-cluster parallel management.
Narada's energy storage BMS uses a quad-core CPU processor with edge computing capabilities. The core management and protection strategies are handled by a dedicated CPU, ensuring that even if part of the CPU or software malfunctions, the system can still respond to EMS scheduling and stack-level protection strategies, guaranteeing safety and control.
Cloud Service Layer
The Cloud Service Layer manages and analyzes big data, with remote telemetry, signaling, adjustment, and control functionalities.
The control signal telemetry cycle of Narada’s energy storage BMS can reach the millisecond level, with measurement signals within one second. This allows after-sales engineers to access operational data and perform data analysis or fault diagnostics without on-site visits. Additionally, devices such as BAU, BCU, and BMU within the Narada BMS support remote OTA upgrades.
Cloud Platform Data Page
Narada Power has conducted a continuous 12-month operation test on the new generation 1500V liquid-cooled active balancing BMS system, assessing its functionality, performance, reliability, safety, and durability. All indicators met the design standards, with some exceeding industry benchmarks. The system is expected to be mass-produced by the end of 2024.




